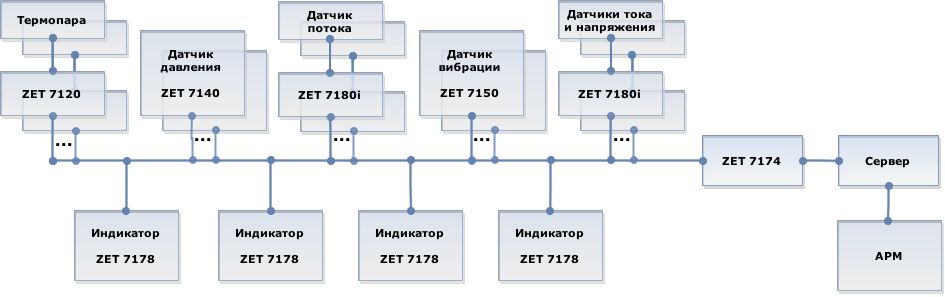
The engine to be tested is placed into a protective casing to be further connected to the test engine. Rotation of the test engine causes rotation of the engine to be tested. The protective casing has ports for connection of circulating water supply, compressed air and temperature sensors (the measurement points are located in direct vicinity to the engine surface).
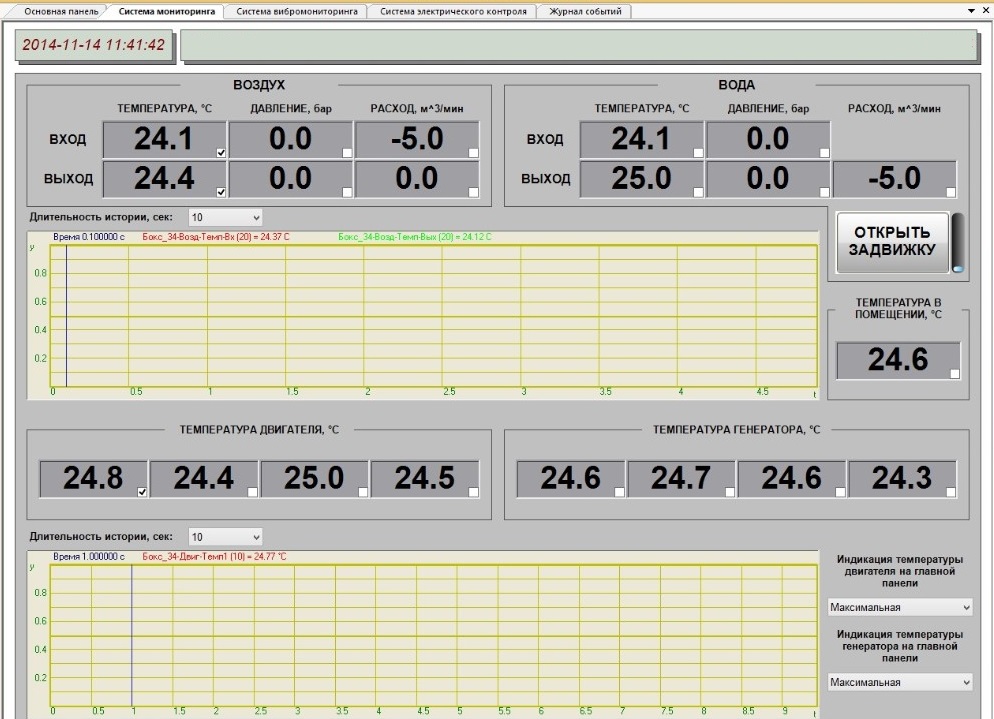
Temperature, pressure and flow sensors are installed at the input and output of cooling liquid and compressed air supply systems.
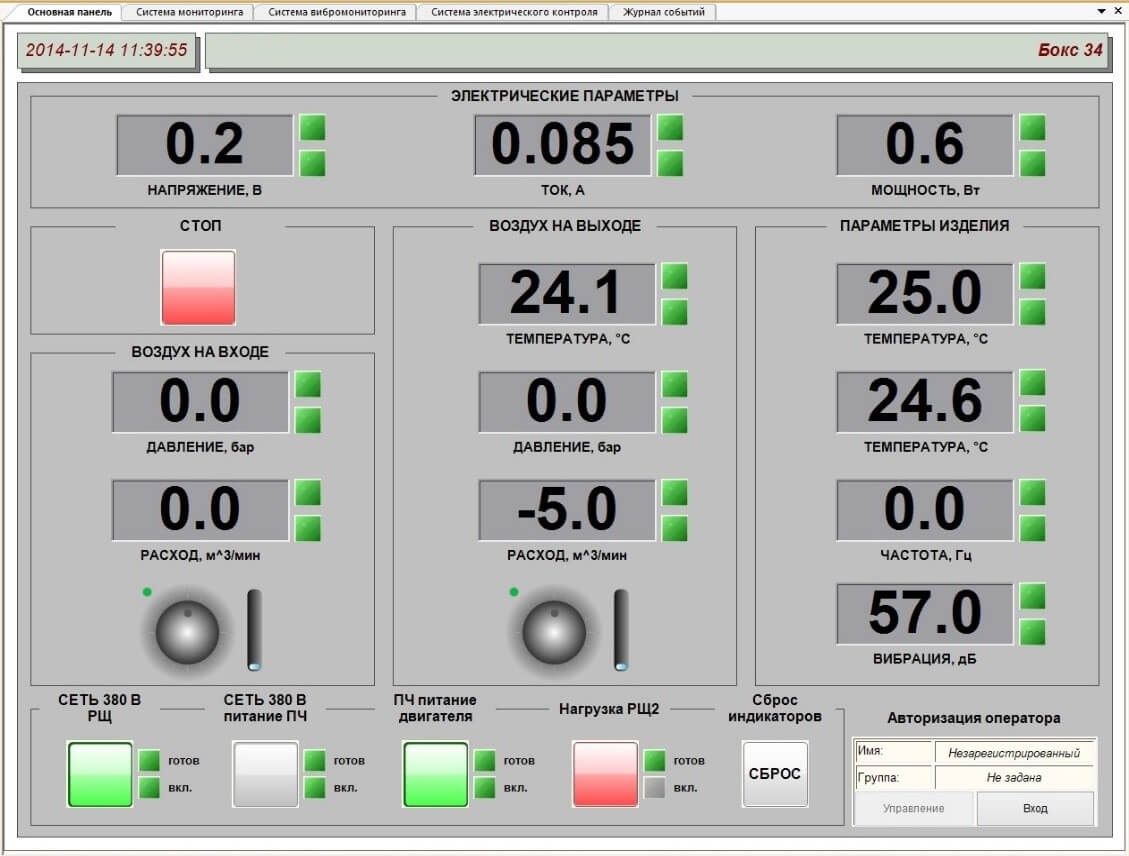
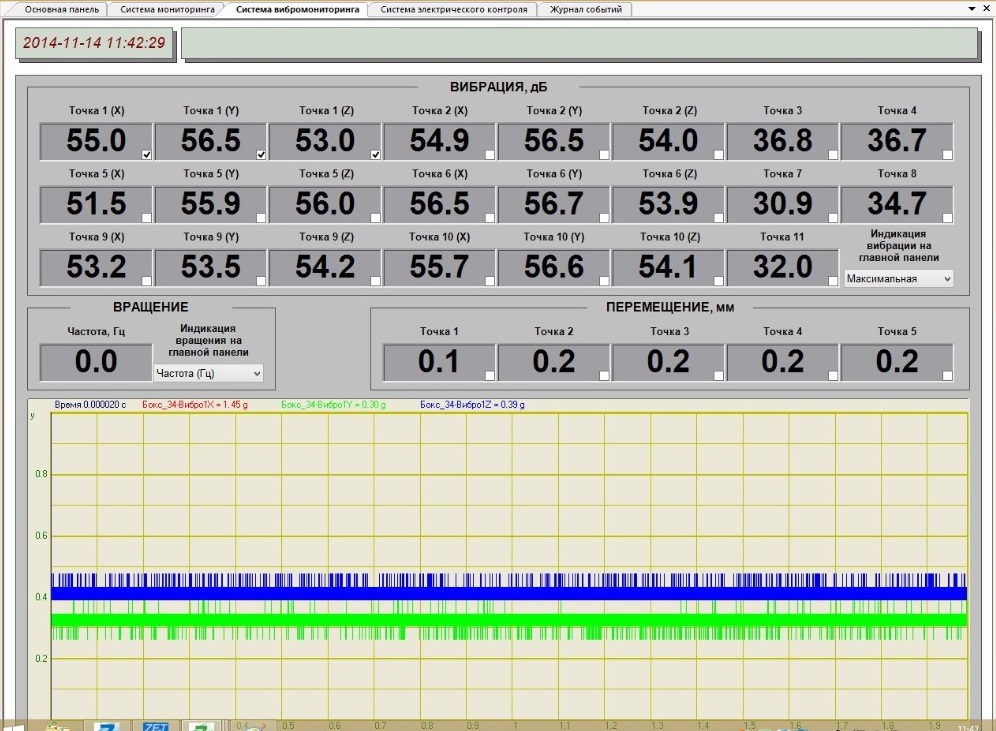
Current and voltage sensors are connected both to the test engine and the engine to be tested as well as to the generator and frequency converter. The vibration sensors are mounted on the test stand supports for the purpose of vibration level control of both test and tested engine.
In the course of system development, there are used digital sensors, consisting of primary transducers (with corresponding measurement units) and measurement modules to be used for processing of the signals received from the primary transducers. In the case of pressure and vibration sensors, the primary transducer and the measurement module are placed inside of a single casing, in other types of sensors they can be placed in separated casings interconnected with cables.
The measuring modules are sequentially connected to the measuring system with cables, thus, forming measurement branches with CAN 2.0 interface. The necessary amount of measurement branches depends on the quantity and location of the tested items.