Virtual measuring instruments
Concept of virtual instruments
The epoch when measuring systems were consisting of a large amount of instruments spread across laboratory room is receding into the past. Modern computers have high performance and are widely available, which allows to use them for implementation of algorithms, that used to be performed by traditional instruments. Thus, the function of a measuring instrument comes down to digital processing of the signals, while data processing and results representation are conducted on a software level.
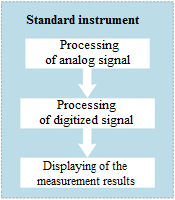
Structural scheme of a standalone measuring instrument
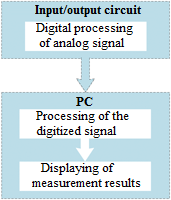
Structural scheme of a virtual instrument
Since functional characteristics of a system based on virtual instruments are determined by a particular software used, ordinary ADC DAC board can be used as voltmeter, oscillograph, generator, strain gauge or any other instrument, thus saving laboratory room and money of the user.
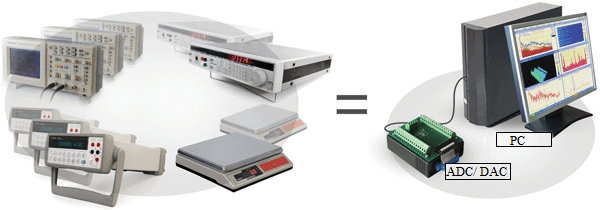
Implementation of ADC/DAC modules and laptops with software having functional range of a laboratory enhances possibilities of field measurements.
Use of wireless technologies in communication between digital processing module and PC enables measurements on a moving object. For instance, ADC/DAC module+Wi-Fi or Bluetooth module can be mounted on a moving object (turbine shaft, vehicle), while PC can be placed at the distance of up to 500 m (depending on the aerial characteristics).
Digital processing of the signals can be performed in standalone mode with recording to a flash-drive (further data processing is conducted as the recorded signals are saved to PC memory). In addition to signal values it is also possible to register such parameters as, e.g., coordinates of the device location. Cartographical programs allow to reproduce the trajectory of object movement in the course of experiment performance along with current location of the controlled object and its parameters at any time period.
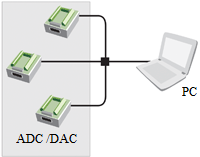
Structural scheme of a distributed data acquisition system
Separation of software and hardware components allows to establish distributed measuring systems. Data acquisition nodes contain ADC/ DAC boards, which are connected to PC via Ethernet network. Synchronization by GPS and/or GLONASS enables simultaneous transfering and processing of data array.
Development of virtual instruments concept ushered a new epoch in automated systems developement. Use of object-oriented software applications allows to create unique applications with analysis system and operating scenarios suitable both for programmists and industrial engineers.
Thus, it is possible to outline the following advantages of virtual instruments:
- reduced costs;
- laboratory room saving;
- parallel analysis of multiple parameters;
- extended application sphere: field measurements, measurements on moving elements, standalone mode;
- development of distributed multichannel systems;
- simplification of automated systems development.
Virtual instruments types
Selection of particular virtual instrument depends on task-specific factors. It is possible to divide the virtual instruments in 3 categories based on their complexity degree:
- Turnkey solution of a particular task – key factor: simplicity of use:
- ZETSCOPE by ZETLAB Company (Russia)
- Virtual laboratory — key factor: multiple functions:
- ZETLAB by ZETLAB Company (Russia)
- Modules for measuring system development — key factor: flexibility:
- LabView by «National Instruments» (USA)
- ZETVIEW by ZETLAB Company (Russia)
Turnkey solutions are equivalents of traditional instruments. Interface of these virtual tools is similar to that of their standalone analogs, so the user does not need any additional training. A drawback of these systems is the lack of flexibility, but they are easy to set and use.
Measuring system modular structure provides the user with maximum possible flexibility in the case if he has certain programming experience. Before starting measuring process, one should “assemble” the virtual instrument from the modules available. A clear advantage of such system is its full conformity to the user’s requirements. These virtual instruments are used for creation of complex control and data acquisition systems.
Prior to development of a new measuring system one should pay attention to virtual laboratories, which encompass most of the necessary instruments meeting applicable requirements. The user has a lot of programs at his disposal, so all he has to do is to set the system in accordance with his personal needs.
Virtual instruments by ZETLAB
ZETLAB software is a virtual laboratory consisting of more than 50 instruments. All the instruments are classified into particular groups depending on their functions: analysis, measurements, display, generators, etc. Various ADC / DAC devices have corresponding program packages with relevant functions and specifications.
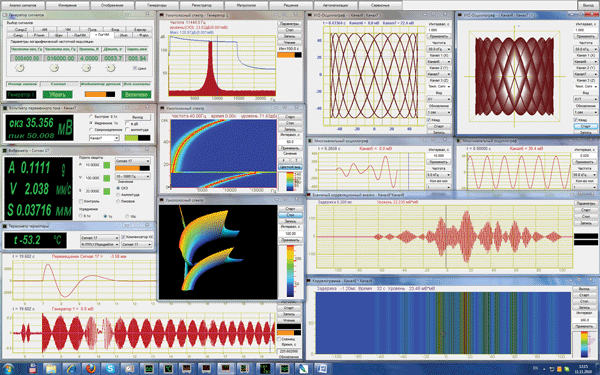
Virtual laboratory ZETLAB
ZETLAB programs have various degrees of complexity. For instance, “Voltmeter” program has only three settings options available: averaging time switch, results representation in dB, RMS / amplitude value switch. “Generator” program has 12 different signal types available: from sine and pulse signals to Barker (each of the signals has addtitional parameters).
In addition to basic instruments (such as voltmeter, generator, etc.), ZETLAB provides powerful instruments for signals processing. ZETFormula program has dozens of mathematical and measuring functions, 20 filter types and can be used for work both with source and processed signals.
ZETLAB software allows to perform data analysis by several programs simultaneously, besides, the programs can be used for processing of each other’s iutput data. For instance, it is possible to filter the digitized signal, perform calculations and to display the final results in 2- and 3-dimensional format.
ZETLAB Software also includes such options as AFR measurements with feedback, controller, events detector, that are using data from other programs (such as voltmeter, temperature meter) with parallel control of the devices connected to PC by means of other programs (e.g. generator, switching module).
Author: T. Konovalova
